DYNERTIAL - clustering and settling dynamics of inertial particles under turbulence
PhD project
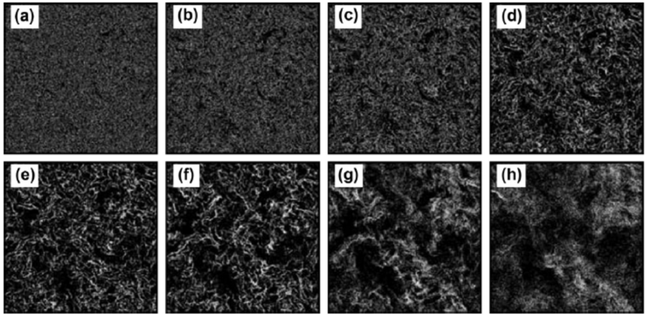
In spite of its apparent simplicity, the physics of finite size spheres advected by a fluid hides a whole hierarchy of rich imbricated phenomena, some of which are still shrouded in mystery. This is for instance the case when a particle is in a turbulent environment and/or when hydrodynamic couplings emerge between many particles, resulting in subtle collective behaviours. Unveiling the fundamental mechanisms of such phenomena remains crucial to improve our capacity to accurately model and predict particle laden flows. These flows are present in many different processes such as coalescence (rain formation), agglomeration (particles in the atmosphere), settling velocity (sedimentation), chemical transformations (risers), among many others.
All such flow configurations present many open fundamental questions and are subject of great interest in current research. Indeed, because of their higher density compared to the carrier fluid, inertial particles interacting with the underlying turbulence tend to form high (clusters) and low (voids) concentration regions (as exemplified in Fig.1a). These regions span almost the whole range of turbulence scales, i.e. from the Kolmogorov length scale up to the integral length scale or even larger for superclusters, and the widest regions exhibit self-similarity. Such non-trivial spatial organization of particles, a phenomenon referred to as preferential concentration, has strong consequences on the flow dynamics by way of momentum exchanges between phases, of velocity fluctuations generation or of collective dynamics, as well as on particle transport and dispersion. Ultimately, these features control the efficiency of all the applications mentioned above.
On a first stage, measuring campaigns in UGA-LEGI (Grenoble, France) and in Univ. Washington (Seattle, USA) facilities are envisioned. Measuring techniques such as Phase Doppler interferometry, Particle Image Velocimetry, Phase detection optical probes are already mastered as well as post-processing routines to access drop size, velocity, concentration and combined statistics as done in our former contributions.
The objective here is to gather new type information from experiments.
- First, we plan to collect Lagrangian statistics of particle velocity conditioned on the local concentration but also conditioned on the particle size that has never been done.
- Second, we will attempt to measure the flow field in the vicinity of particles to gather conditional statistics of the settling velocity with the local fluid velocity and acceleration.
From the results from previous work packages, attempts will be made to derive some ad-hoc modeling to account for particle-turbulence interaction and collective effects on the settling velocity and on dispersion.
The expected outputs are the following:
- clarify the mechanisms leading to clusters/voids formation in relation with turbulent flow structures and determine how clusters/voids characteristics (size, concentration, shape…) evolve with flow parameters,
- determine the properties of particles settling velocity and how it Is affected by turbulence,
- identify scaling law(s) for the settling velocity modification due to particle-turbulence interactions by disentangling the contributions of fluctuations in velocity and in acceleration of the carrier phase,
- identify the effect of volume concentration on cluster characteristics and on the competition between collective effects and loitering and v) establish empirical or phenomenological models of these behaviors.
In spite of its apparent simplicity, the physics of finite size spheres advected by a fluid hides a whole hierarchy of rich imbricated phenomena, some of which are still shrouded in mystery. This is for instance the case when a particle is in a turbulent environment and/or when hydrodynamic couplings emerge between many particles, resulting in subtle collective behaviours. Unveiling the fundamental mechanisms of such phenomena remains crucial to improve our capacity to accurately model and predict particle laden flows. These flows are present in many different processes such as coalescence (rain formation), agglomeration (particles in the atmosphere), settling velocity (sedimentation), chemical transformations (risers), among many others.
All such flow configurations present many open fundamental questions and are subject of great interest in current research. Indeed, because of their higher density compared to the carrier fluid, inertial particles interacting with the underlying turbulence tend to form high (clusters) and low (voids) concentration regions (as exemplified in Fig.1a). These regions span almost the whole range of turbulence scales, i.e. from the Kolmogorov length scale up to the integral length scale or even larger for superclusters, and the widest regions exhibit self-similarity. Such non-trivial spatial organization of particles, a phenomenon referred to as preferential concentration, has strong consequences on the flow dynamics by way of momentum exchanges between phases, of velocity fluctuations generation or of collective dynamics, as well as on particle transport and dispersion. Ultimately, these features control the efficiency of all the applications mentioned above.

CONTACTS
- PI: Martin Obligado
- Co-PI: Alberto Aliseda
- PhD: Daniel-Andres Mora Paiba

PARTNERS
- LEGI
- Department of Mechanical Engineering, Univ. Washington, Seattle

FUNDING
- Tec21
- Univ. Washington
- IDEX Grenoble
